- Хазанович-Вульф К.К. (2007). Диатремовые шлейфы астроблем или "болидная модель" образования кимберлитовых трубок. Из-во "Геомастер", Петрозаводск, 272с.
- Хазанович-Вульф К.К. (2011). Астероиды, кимберлиты, астроблемы. , Санкт-Петербург, 192 с.
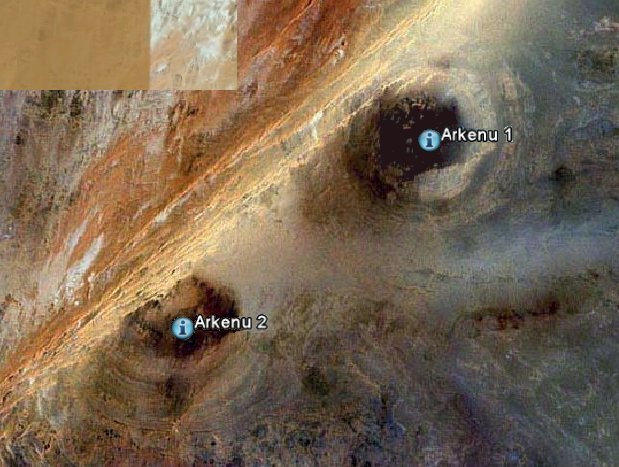
- Paillou Philippe, Rosenqvist Ake, Malezieux Jean-Marie, Reynard Bruno, Farr Tom, Heggy Essam (2003). Discovery of a double impact crater in Libya: the astrobleme of Arkenu. Academie des sciences, Paris // C. r. Geosci, Vol.335, No.15, 1059-1069
- John G. Spray, Director PASSC (2005). Impact Structures listed by Name. Current total number of confirmed impact structures: 172.
- Osinski Gordon R. (2006). The geological record of meteorite impacts. 40th ESLAB First International Conference on Impact Cratering in the Solar System, 8-12 May 2006., Noordwijk,The Netherlands
- Norbert Brugge (2004). Remarks to the origin of the craters around Gilf Kebir and Djebel Uweinat (Egypt) and the supposed impact craters of Libya // Dipl. Geol.
- Reimold W.U., Koeberl Ch. (2014). Impact structures in Africa: A review // J. Afr. Earth. Sci. 93: 57-175.
 cm.
cm.
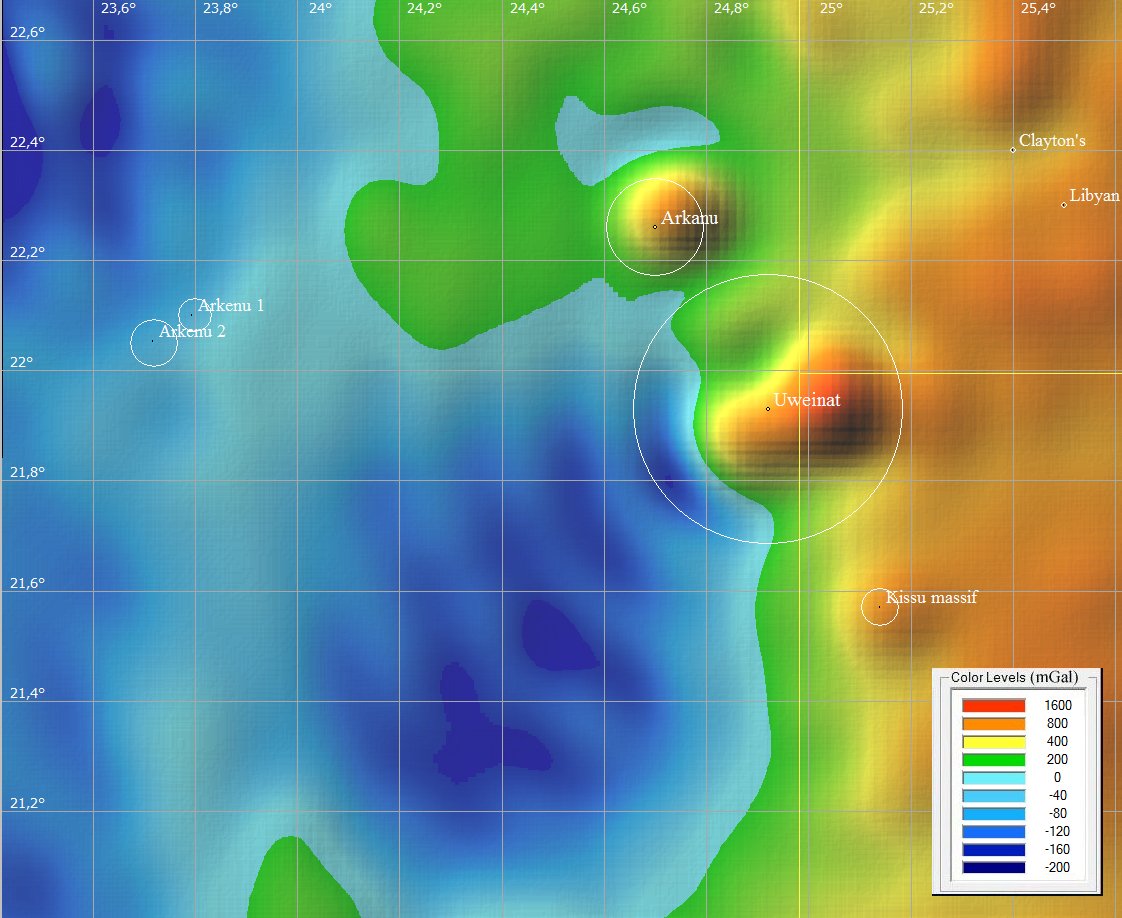
Аномалии силы тяжести в районе кратера (получено по данным GLOBAL MARINE GRAVITY V18.1 средствами системы ENDDB).
Реферат:
В Северной Африке установлено несколько парных кратеров одинакового возраста, что позволяет определить направления прилета МТ для поисковых работ на диатремы. Это:
1) Оазис (18 км) и В.Р.S. (2 км), Ливия, <120 млн. лет;
2) Аркену-1 (6,8 км) и Аркену-2 (10 км), Ливия,< 140 млн. лет.
(Хазанович-Вульф К.К., 2007).
На главную
 cm.
cm.

 cm.
cm.
